Key Findings at Look
|
We surveyed 1,000 house owners and managers of small companies (50 or fewer staff), nationwide about web site safety. What we discovered: 12% have obtained a ransom demand associated to their web site, e-mail, or information — and paid it.
Why does this matter?
Small companies symbolize low-hanging fruit for cybercriminals, making these assaults more and more frequent. Our findings reveal how widespread — and dear — the menace has grow to be for on a regular basis enterprise house owners, not simply giant enterprises.
As a webhosting supplier that serves hundreds of small companies, DreamHost wished to know the real-world impression of those threats and the way ready companies are to reply. The outcomes level to clear gaps — and actionable options — in small enterprise cybersecurity.
Image a room of 100 individuals who run web sites: freelancers, retailer operators, small enterprise house owners; of us who simply need their web site to work. Now depend off twelve of them.
The information reveals that 12 out of each 100 web site operators have paid a ransom to regain entry to their websites or information. When web sites go offline on account of cyberattacks, companies face speedy operational disruptions: inaccessible administrative panels, unfulfilled orders, and locked buyer information.
For a lot of, paying the ransom seems to be the quickest path to restoration, regardless of low attacker compliance charges.
The priority extends past those that have paid. 42% of respondents reported being “very involved” about ransomware assaults concentrating on web sites, reflecting widespread consciousness of the menace panorama.
The complete survey information reveals why that concern is justified — and what companies can do about it.
Let’s get into it.
1 in 8 People Have Paid a Ransom

That 12% represents companies at a call level: pay the ransom or face extended downtime.
Every fee reinforces the ransomware enterprise mannequin, validating the tactic and growing the chance that extra companies will face comparable calls for.
Ransomware assaults are usually not restricted to giant enterprises. Small companies with accessible on-line infrastructure face the identical threats.
A more in-depth take a look at those that obtained ransom calls for reveals the function preparedness performs in decision-making.
Of the 28.4% who confronted a requirement, 41.5% paid the ransom. When going through that second — web site down, information locked, income frozen — practically half select to pay.

On the flip aspect: 58.5% refused. That’s 6 in 10 companies who declined to pay.
The information suggests that companies with examined backups, restoration protocols, and operational resilience had been extra more likely to refuse fee. Infrastructure preparedness seems to cut back vulnerability to ransom calls for.
Companies that perceive their dangers and preserve examined backups, safe logins, and automatic restoration methods reveal decrease susceptibility to those assaults.
Practically Half of People are Deeply Anxious About Ransomware Threats
42% of respondents in our survey mentioned they’re “very involved” concerning the rising menace of ransomware assaults concentrating on web sites. Mixed with those that are “very involved” with those that are “considerably involved,” 84.6% of respondents see ransomware as a official menace.
The web site is the enterprise — the storefront, the pipeline, the hub. Disruption to entry can straight impression enterprise operations.
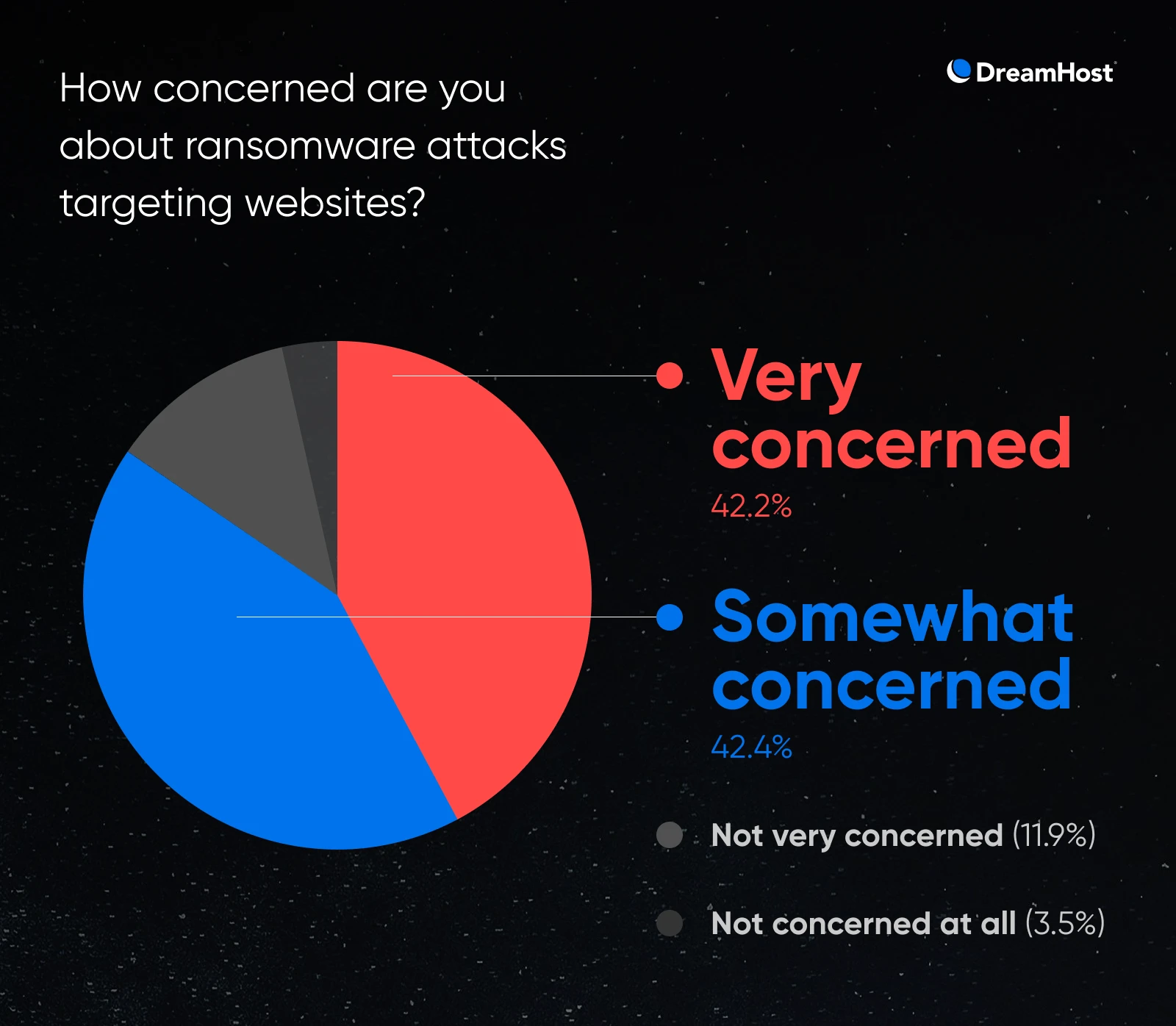
This apprehension displays a broader shift: ransomware has expanded past giant enterprises to focus on small companies.
Excessive-profile breaches illustrate the scope of the menace.
When AT&T skilled a breach affecting 73 million present and former prospects — together with their Social Safety numbers, beginning dates, and names — the corporate confronted a $177 million settlement. The breach, relationship again to 2019, was solely acknowledged after buyer information appeared on the darkish net.
If organizations with devoted safety groups expertise breaches of this scale, small companies face comparable vulnerabilities with out comparable assets for proactive safety.
The writing’s on the wall: neglect invitations publicity.
Our survey information reveals that many enterprise house owners acknowledge frequent safety weaknesses: outdated plugins, weak passwords, and uncared for CMS updates. This consciousness is driving elevated consideration to cybersecurity practices amongst small companies.
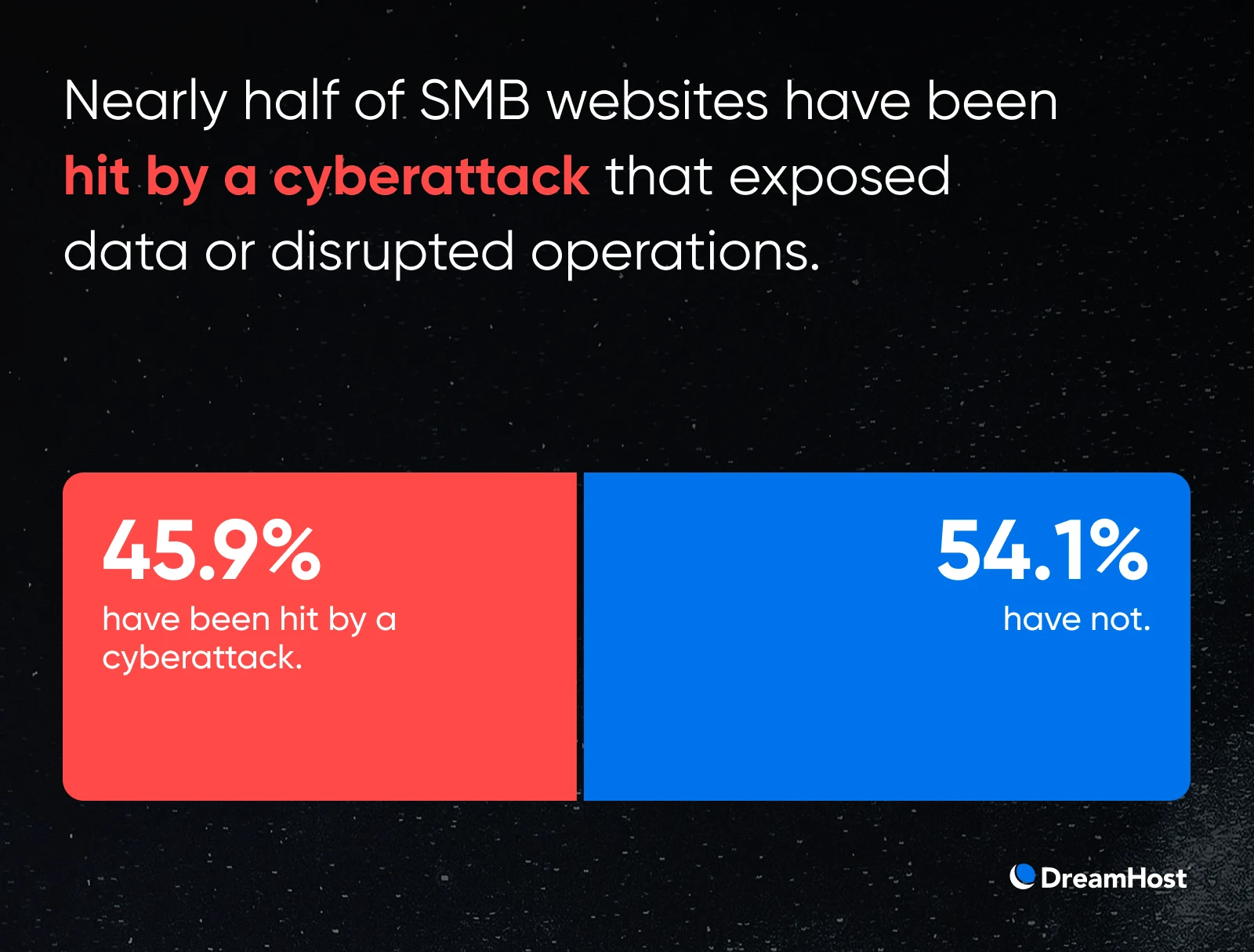
Practically Half of Companies Have Already Been Hacked
That widespread concern isn’t unfounded. 46% of our respondents have already skilled a cyberattack, leading to uncovered information, encrypted recordsdata, or full web site shutdowns.
For 38% of respondents, these assaults got here within the type of on a regular basis breaches that hardly ever make headlines however can result in:
- Compromised logins
- Contaminated plugins
- website positioning spam redirects
- Suspended domains
Every can imply misplaced income from downtime, broken search rankings, and eroded buyer belief — issues that compound shortly for small companies working on skinny margins.

Malware infections, particularly, can unfold shortly via outdated plugins and themes, and for 14% of those that’ve been hacked, it’s not a one-time occasion — they’ve skilled a number of assaults.
The information reveals that counting on an online host’s built-in safety isn’t sufficient, and the price of restoration far exceeds the price of prevention. But many proceed working with the identical vulnerabilities that received them breached within the first place — ignoring updates, skipping safety audits, and utilizing weak credentials.
These incidents usually function precursors to bigger ransomware occasions. Many web site house owners method cybersecurity reactively reasonably than proactively.
1 in 4 People By no means Take a look at Their Web site Backups

Even after being hacked or seeing friends expertise information loss, many companies nonetheless haven’t verified that their web site backups really work. Practically one in 4 respondents (24%) reported they’ve by no means examined their backup and restore course of.
That hole between having a plan and having a plan that works is the place minor crises grow to be main enterprise disruptions.
Many homeowners assume “auto-backup” means “auto-recovery.”
It doesn’t.
Backups can fail silently or grow to be corrupted. Testing a backup takes lower than quarter-hour and could possibly be the distinction between a short inconvenience and weeks of downtime.
40% of People Would Pay for Backups To Keep away from Paying Hackers
There’s a optimistic development within the information: 40% of respondents mentioned they’d be probably to put money into automated web site backups if it meant they might keep away from paying a ransom.

This represents a shift towards prevention as a monetary choice. Practically 1 / 4 of respondents cited price or complexity because the barrier conserving them from backup options. Nevertheless, automated backups price considerably lower than restoration from an information breach.
4.6% mentioned they’d by no means put money into backups in any respect. These companies stay susceptible to ransomware assaults.
The common complete price for a small enterprise to reply to and get well from an information breach can vary from $120,000 to $1.24 million.
When a web site might be restored in minutes, ransom calls for lose their effectiveness. The sooner restoration occurs, the much less leverage attackers have. This positions backup instruments as important infrastructure. If a web site might be restored shortly, attackers lose their main bargaining instruments: time and entry.
Abstract
Practically half of small companies have already skilled a cyberattack. This widespread menace is driving a shift in how companies method cybersecurity: consciousness is now excessive, and web site house owners more and more view cybersecurity as continuity planning, not simply technical price.
The trail ahead is obvious. Resilience is constructed with disciplined preparation: rigorously examined backups, instruments that automate protection, and a dedication to digital preparedness.
The simplest protection is fast response and restoration functionality.
Companies that put together upfront face considerably decrease danger when assaults happen.
Methodology
This text relies on a nationwide survey performed in October 2025, wherein we collected responses from 1,000 People to raised perceive their experiences and issues associated to web site safety and cyber threats. The survey particularly focused people who personal or handle companies with 50 or fewer staff, making certain the info displays the distinctive challenges and realities confronted by small enterprise operators.
Individuals represented a various cross-section of industries {and professional} backgrounds, providing a well-rounded snapshot of public sentiment and real-world impacts. Respondents had been requested a sequence of questions on ransomware, web site breaches, information safety practices, and incident response, offering beneficial insights into the present state of cybersecurity consciousness and preparedness amongst small enterprise house owners within the U.S.
Truthful Use
Customers are welcome to make use of the insights and findings from this examine for non-commercial functions, akin to educational analysis, academic displays, and private reference. When referencing or citing this text, please guarantee correct attribution to keep up the integrity of the analysis. Direct linking to this text is permissible, and entry to the unique supply of knowledge is inspired.
For industrial use or publication functions — together with however not restricted to media shops, web sites, and promotional supplies — please contact our Company Communications staff for permission and licensing particulars.
We admire your respect for mental property rights and adherence to moral quotation practices. Thanks in your curiosity in our analysis.
Did you take pleasure in this text?

![[STUDY] 12% of Small Companies Say They’ve Paid a Ransom Demand [STUDY] 12% of Small Companies Say They’ve Paid a Ransom Demand](https://i1.wp.com/www.dreamhost.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/1460x1095_blog_hero_12_of_small_businesses_say_they_ve_paid_a_ransom_demand.webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)