When most individuals hear robotic, they image a shiny humanoid with glowing eyes, steel limbs, and a stiff stroll straight out of science fiction. However robotics is way broader and older than that stereotype.
Lengthy earlier than AI assistants and silicon chips, early inventors have been crafting intricate machines powered by steam, springs, and ingenuity. Quick ahead to right now, and robots are in every single place: constructing vehicles, helping surgeons, navigating warehouses, and sure, even vacuuming our dwelling rooms.
However as robotics continues to broaden into software-driven areas like Robotic Course of Automation (RPA), the place bots reside in your browser, not in your manufacturing facility flooring, it’s straightforward to get misplaced within the terminology.
That’s why we created this robotic glossary. A full A to Z information to robotics phrases, defined clearly, with examples and a contact of humor. Whether or not you are studying an educational paper or decoding what your tech-savvy coworker means by finish effector, this glossary has you lined.
Who coined the time period “robotic”?
Czech author Karel Čapek coined the time period “robotic” in his 1920 play R.U.R. (Rossum’s Common Robots). The phrase was derived from the Czech phrase “robota,” which means pressured labor. Though the concept got here from his brother Josef, Karel Čapek popularized it in literature.
Whether or not you are a pupil, knowledgeable within the area, or simply interested in robots, this glossary will enable you to make sense of core robotics terminology. Need to see how these phrases advanced? Discover the historical past of robotics to hint the roots of right now’s robotic know-how.
TL;DR: The whole lot it’s good to learn about robotic phrases
- What are an important robotics phrases to know? This glossary covers important robotics terminology throughout mechanics, management programs, and synthetic intelligence.
- What do phrases like actuator, finish effector, or humanoid imply? Study clear definitions for frequent robotics parts and ideas — from A to Z.
- Who is that this robotics glossary for? Whether or not you are an engineer, educator, pupil, or fanatic, this information makes robotics phrases accessible and sensible.
- How are robotics phrases utilized in the true world? Uncover how these phrases apply in actual use circumstances, from manufacturing facility flooring and healthcare to autonomous automobiles.
- What’s the distinction between robotics and automation or RPA? Perceive how robotics suits into the broader world of automation and the place software program bots diverge from bodily machines.
Robotic phrases A by E
A
Actuator: The “muscle” of the robotic. It converts management indicators into motion, rotating, lifting, or pushing parts into motion. Powered by electrical motors, hydraulics, or pneumatics.
Adaptive Management: A kind of management system that permits robots to change their habits in actual time based mostly on environmental suggestions. Helpful for unpredictable or dynamic duties.
Aerobot: An aerial robotic able to flying autonomously, typically utilized in environmental monitoring, surveillance, or drone-based supply programs.
Algorithm: A set of programmed guidelines or directions {that a} robotic follows to make choices or perform duties. Algorithms are the core of robotic intelligence and motion planning.
Android: A humanoid robotic designed to resemble an grownup human male. The ‘andro’ prefix is in reference to the assigned masculine gender of the machine.
Articulated manipulator: A robotic arm with a number of joints (like a human shoulder, elbow, wrist) that permits it to maneuver in a number of instructions. Widespread in manufacturing and welding strains.
Automaton: A mechanically pushed gadget that mimics life or performs repetitive duties. Standard in historical engineering, some even powered by water or clockwork.
Autonomous automobile: A self-driving robotic (automotive, drone, rover) that navigates and makes choices with out human management, utilizing sensors, GPS, and onboard AI.
Axis/diploma of freedom: Describes what number of instructions or rotations a robotic can transfer in. A typical robotic arm may need 6 levels of freedom, permitting for advanced, lifelike movement.
B
Battery Administration System (BMS): Software program and {hardware} that monitor and handle a robotic’s battery efficiency, stopping overheating or overcharging.
Bionics: The combination of organic ideas into robotics, like mimicking how muscle tissue work or how bugs stroll to enhance robotic design.
C
perform of a cartesian robotic artwork, courtesy of toshiba.com
Cartesian manipulator: A robotic that strikes in straight strains alongside the X, Y, and Z axes. Assume 3D printers or CNC machines, exact, linear, and very best for pick-and-place duties.
Central processing unit: The robotic’s “mind.” It interprets indicators from sensors and controls actions throughout the system.
Chassis: The structural body or base of a robotic on which parts like actuators, sensors, and processors are mounted.
Cloud robotics: Robots that depend on cloud computing to course of knowledge or coordinate habits, very best for fleets of linked bots or light-weight designs.
Cobots: Brief for collaborative robots, these are designed to work safely alongside people. Typically used on combined manufacturing strains or in healthcare.
Collision Detection: A security system that permits robots to acknowledge and keep away from contact with objects, people, or different robots. Typically tied to imaginative and prescient or proximity sensors.
Compliance: A robotic’s capability to yield or adapt to drive or sudden interference, typically engineered in for security or delicate work.
Controller System: The overarching pc system that directs the robotic’s actions, storing applications, working calculations, and managing sensors and actuators.
Cyborg: A mix of “cybernetic” and “organism”, half machine, half human. Assume neural implants, robotic limbs, or wearable exoskeletons.
D
Levels of Freedom (DOF)” Whereas “Axis/diploma of freedom” is already talked about, this deserves its personal entry because it’s a foundational robotics idea, the variety of impartial actions a robotic can carry out.
Drive System: The mechanism that propels a cell robotic, could possibly be wheels, tracks, or legs. Widespread drive sorts embody differential, omnidirectional, and Ackermann steering.
Downtime: When a robotic is not working on account of failure, upkeep, or reprogramming. A important metric in manufacturing environments.
E
Edge Computing: A technique the place robots course of knowledge domestically (on the robotic itself) moderately than counting on cloud servers. Reduces latency and allows sooner real-time choices.
Encoder: A sensor that tracks the place or rotation of a motor shaft, enabling exact movement management in robotic joints or wheels.
Finish effector: The software on the finish of a robotic arm. Could be a gripper, welder, paint sprayer, or surgical instrument relying on the duty.
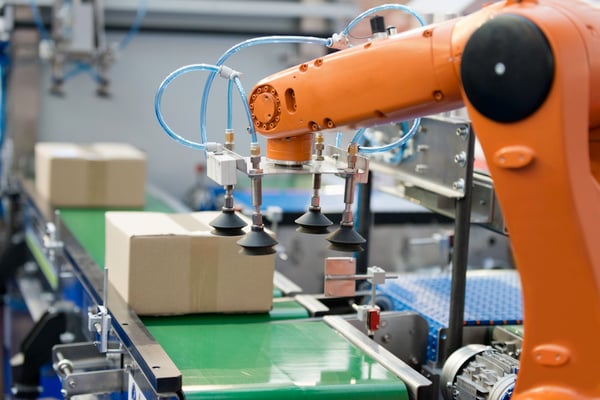 An instance of an end-effector on an industrial robotic (supply: robotics.org)
An instance of an end-effector on an industrial robotic (supply: robotics.org)
Robotics phrases F by Ok
F
Suggestions sensor: Gives real-time environmental or mechanical knowledge to the robotic, serving to it regulate actions or choices dynamically.
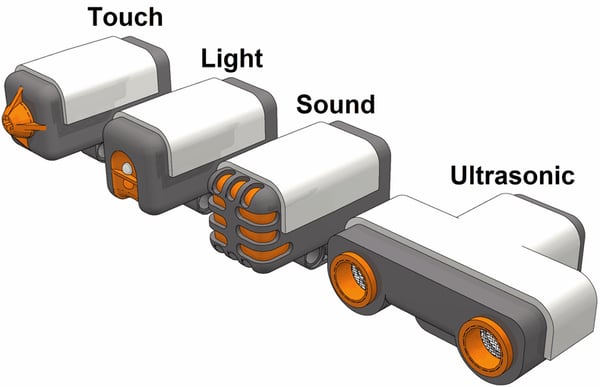 Completely different variants of robotic sensors (supply: http://iggyclass.blogspot.com)
Completely different variants of robotic sensors (supply: http://iggyclass.blogspot.com)
Power limiting: A security function that caps how briskly or laborious a robotic can transfer, stopping harm throughout human interplay.
Power Sensor: Measures strain or drive exerted by the robotic, helpful for fragile duties like assembling electronics or pouring drinks.
G
Gantry: A big, overhead help construction that lets a robotic transfer alongside mounted rails. Typically used for high-precision or heavy-duty industrial robots.
Gynoid: A female-presenting humanoid robotic. The counterpart to androids, usually utilized in analysis or media portrayals of robotics.
 Instance of a feminized robotic from the online game Starcraft II
Instance of a feminized robotic from the online game Starcraft II
H
Haptic: Contact-based suggestions used to offer robots sensitivity to surfaces and drive. Allows delicate duties like dealing with glass or medical instruments.
Harness: Wiring and cables bundled collectively to ship energy and knowledge all through a robotic.
Hexapod: A six-legged strolling robotic modeled after bugs. Identified for stability and flexibility on tough terrain.

Humanoid: Any robotic with a physique plan just like a human. Consists of each androids and gynoids and used for superior AI interplay and mobility analysis.
Hydraulics: Makes use of pressurized fluid to generate mechanical motion. Widespread in heavy-load robots or exoskeletons.
I
Industrial robotic: Robots purpose-built for manufacturing. Assume welding arms, packaging bots, or pick-and-place machines on an meeting line.
Enter gadget: A management or programming interface — joystick, contact panel, keyboard — that permits people to direct or train robotic habits.
Clever robotic: A robotic that may adapt based mostly on sensor knowledge or prior expertise. Combines robotics with AI to carry out advanced, unstructured duties.
J
Jacobian matrix: A mathematical software used to calculate how a robotic’s joint actions translate into finish effector motion. Essential in robotic movement planning.
Robotic phrases L by Z
L
Laser: Utilized in robots for measuring distance, guiding reducing paths, or exact welding. Additionally frequent in autonomous navigation (LiDAR programs).
N
Nanobot: Microscopic robots (typically theoretical or experimental) constructed on the nanoscale, utilized in medication, chemistry, or supplies science.
P
Payload: The utmost weight a robotic can carry with out efficiency loss. Key consider deciding on robots for lifting or transport duties.
Pinch Factors: Hazardous areas in robotic joints the place limbs or clothes could possibly be caught. Typically marked with warning labels.
Pneumatics: Generates robotic movement utilizing compressed air. Quieter and cleaner than hydraulics, typically utilized in light-weight or delicate bots.
Powered Exoskeleton: Wearable robotics designed to boost human power or mobility. Utilized in rehabilitation, navy, and industrial lifting.
The mech is a sci-fi staple and dramatic instance of what exoskeletons might at some point be
Prosthetic: A robotic or programmable limb substitute. Trendy variations embody sensor inputs and adaptive movement for amputees.
R
Robotic: A machine able to finishing up duties independently, based mostly on programmed directions or environmental suggestions.
RPA: Software program bots that carry out repetitive digital duties, no bodily robotic concerned. Widespread in finance, HR, and customer support.
S
Sensor: Gadgets that permit robots “see,” “really feel,” or “hear” their surroundings. Consists of cameras, strain sensors, proximity detectors, and extra.
Singularity: A degree the place a robotic’s arm joints align in a manner that limits motion. To not be confused with the AI singularity!
U
Uptime: The other of downtime, how lengthy a robotic operates with out interruption. Excessive uptime is an indication of dependable efficiency.
Kinds of robots defined: What are the totally different varieties?
To make sense of robotics phrases, it helps to first perceive how robots are categorized. This is a breakdown of the commonest robotic sorts you’ll encounter:
Industrial robots
These are the spine of factories worldwide, constructed for velocity, precision, and repetition. Whether or not it’s welding automotive frames or assembling smartphones, industrial robots get the job accomplished.
Examples:
- Robotic arms with finish effectors
- Cartesian or SCARA robots
- Heavy-load machines for fabrication
Key phrases: Actuator, payload, finish effector, downtime
Service robots
Service robots work instantly with individuals in houses, places of work, and public areas. They vacuum flooring, ship room service, and even verify in lodge visitors.
Examples:
- Cleansing bots
- Reception robots
- House assistants
Key phrases: Cobots, haptic, suggestions sensor
Autonomous robots
These bots assume (just a little) for themselves. Utilizing AI, sensors, and software program, autonomous robots can navigate environments and adapt to altering inputs, no distant management wanted.
Examples:
- Self-driving supply robots
- Drone swarms
- Warehouse navigation bots
Key phrases: Cloud robotics, suggestions sensor, clever robotic
Humanoid robots
Formed like us, and typically eerily lifelike. Humanoid robots embody androids (male-formed) and gynoids (female-formed), they usually’re typically utilized in AI analysis and leisure.
Examples:
- Social robots
- Analysis androids
- Interactive humanoids in media
Key phrases: Android, gynoid, humanoid, articulated manipulator
Robotics vs. Automation: What’s the distinction?
These phrases get tossed round lots, typically interchangeably, however they imply various things.
Robotics
Robotics is all about bodily machines that may transfer, sense, and act. Robots usually embody {hardware}, software program, and actuators to hold out duties with out direct human management.
Automation
Automation refers back to the broader idea of constructing programs run with out human intervention. It may be mechanical, software-driven, or contain robots, however doesn’t require them.
RPA vs. Bodily robots
Let’s clear up an enormous level of confusion: RPA has nothing to do with bodily robots.
| Time period | What it means | Instance |
| Robotic | A programmable machine that interacts bodily | A robotic arm welding automotive frames |
| Automation | Any system that operates with out guide management | An automatic sprinkler system |
| RPA | Software program bots that mimic digital duties | Like a digital assistant copying invoices right into a CRM |
How robots are utilized in real-world industries
Robots aren’t simply sci-fi; they’re reshaping how total industries work. Right here’s the place they’re making an affect:
Healthcare
- Surgical robots like Da Vinci programs help with precision duties
- Rehab bots assist sufferers regain motion
- Prosthetics provide robotic replacements for limbs
Manufacturing
- Industrial arms deal with welding, packaging, and portray
- Cobots help human employees safely
- Sensors detect product defects in actual time
Logistics
- Autonomous cell robots (AMRs) transfer items in warehouses
- Drones conduct stock or ship packages
- Cloud coordination permits fleet-wide optimization
Rising Sectors
- Agriculture: robots monitor soil and harvest crops
- Army: drones and battlefield bots
- Hospitality: room supply bots and concierge assistants
Steadily requested questions (FAQs) about robotic phrases
Have extra questions? Discover the solutions right here.
Q1. What are the important thing parts of a robotic?
The important thing parts of a robotic are sensors, actuators, a management system, energy provide, and finish effectors. Sensors collect knowledge, actuators transfer components, the management system processes enter and controls habits, the facility provide offers vitality, and finish effectors carry out particular duties like gripping or welding.
Q2. What’s the distinction between robotics and automation?
The primary distinction between robotics and automation is that robotics entails machines that may be programmed to carry out duties autonomously, whereas automation refers to utilizing know-how to finish processes with minimal human intervention. Robotics typically falls below automation however focuses on versatile, adaptive bodily machines.
Q3. How do sensors work in robotics?
Sensors in robotics work by detecting bodily inputs like gentle, temperature, distance, or movement and changing them into electrical indicators. These indicators are processed by the robotic’s management system to make choices or regulate habits. Sensors allow robots to understand and work together with their surroundings precisely.
This fall. What are cobots, and the way are they used?
Cobots, or collaborative robots, are robots designed to work safely alongside people. They’re utilized in manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and meeting strains to help with duties like lifting, positioning, or inspecting components. Cobots improve productiveness by combining human flexibility with robotic precision and consistency.
Q5. What are the 5 main fields of robotics?
The 5 main fields of robotics are mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, pc science, management programs, and synthetic intelligence. Mechanical engineering designs the robotic’s construction, electrical engineering powers and connects parts, pc science applications habits, management programs handle motion, and AI allows notion and decision-making.
The trail to information
Now that you simply perceive these generally looked for robotics phrases, it is best to know every little thing it’s good to to be able to discover the most recent developments in robotics and AI! Whilst you’re at it, check out a number of the varieties of robots to get sense of what individuals are speaking about within the area right now.
Curious about studying extra about robotics? Uncover how Isaac Asimov’s three legal guidelines of robotics have been used for many years to program morality.
This text was initially revealed in 2021. It has been up to date with new data.

