Virtually every part has a wonderful consumer interface nowadays. Simply level and click on to get issues carried out. So we virtually by no means want the command line.
However the second you join a VPS, you should study these important Linux instructions, otherwise you’ll be left looking at a black display, questioning what the heck to do subsequent.
Whereas there are literally thousands of Linux instructions, I’ve filtered right down to the 30 most-used instructions for day-to-day server administration.
Perceive Your Present Proficiency With Linux Instructions
Relying on how typically you employ Linux instructions, you’ll fall into one in every of these 4 proficiency ranges.
- Basis stage: You possibly can SSH into your server and navigate directories, however you aren’t comfy with system modifications. You in all probability copy-paste instructions from tutorials with out absolutely understanding what they do. File permissions are nonetheless complicated, and when one thing breaks, you don’t know the place to begin trying.
- Skilled stage: You’re comfy with fundamental file operations and may troubleshoot easy points, however complicated issues nonetheless ship you looking for assist. You possibly can handle growth environments however lack the arrogance to optimize efficiency or implement safety measures.
- Infrastructure stage: You possibly can diagnose efficiency bottlenecks and deal with safety configurations, however automation feels overwhelming. You perceive how particular person instructions work, however aren’t fluent sufficient but to mix them into environment friendly workflows.
- Professional stage: You possibly can assume systematically about server structure and may shortly establish the basis reason for complicated points. You automate routine duties and may optimize servers for particular use instances with out counting on exterior assets.
I’ve categorized the Linux instructions under, protecting in thoughts these actual proficiency ranges.
Basis Degree: Instructions Each Developer Should Grasp
The primary time you SSH right into a VPS, you should know find out how to navigate round and have a look at information. These instructions enable you to do this with out feeling utterly misplaced.
Navigation and File Inspection
1. Is: Reveals the contents of your present listing
The command with out parameters lists (get it? ls = record!) all seen information and folders in your present location.
However when managing web sites, you want extra detailed info, so you should utilize ls -la to see permissions, possession, file sizes, and hidden information that begin with dots.
ls -la /var/www/html
The output reveals every part you want:
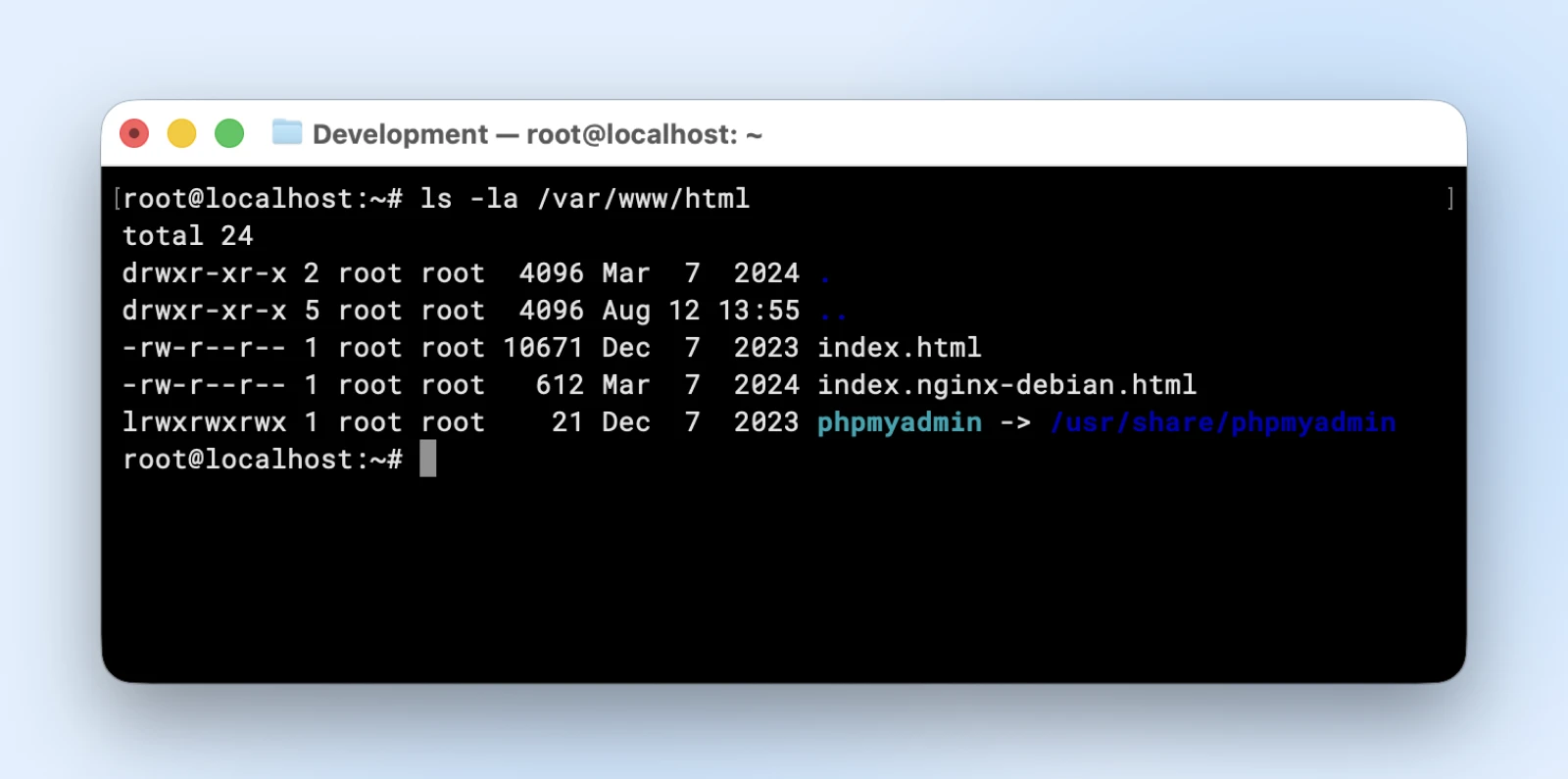
The primary column reveals file permissions, the third and fourth present who owns the file, and the final reveals when it was modified.
The desk reveals detailed details about all information in your internet listing, together with hidden configuration information like .htaccess that may trigger web site points.
2. pwd: Reveals your present location within the listing construction
The command stands for “print working listing” and shows the total path of the place you’re presently situated. When managing a number of web sites on one VPS, this prevents you from by chance enhancing the unsuitable website’s information. Simply sort in:
pwd
This would possibly return one thing like /var/www/site1, confirming you’re working within the right web site listing.
3. cd: Change listing, which modifications your present listing to a special location
The essential syntax is “cd /path/to/listing.”
You should utilize shortcuts like “cd” alone to go house, “cd -” to return to your earlier listing, and “cd ..” to maneuver up one stage.
cd /var/www/html
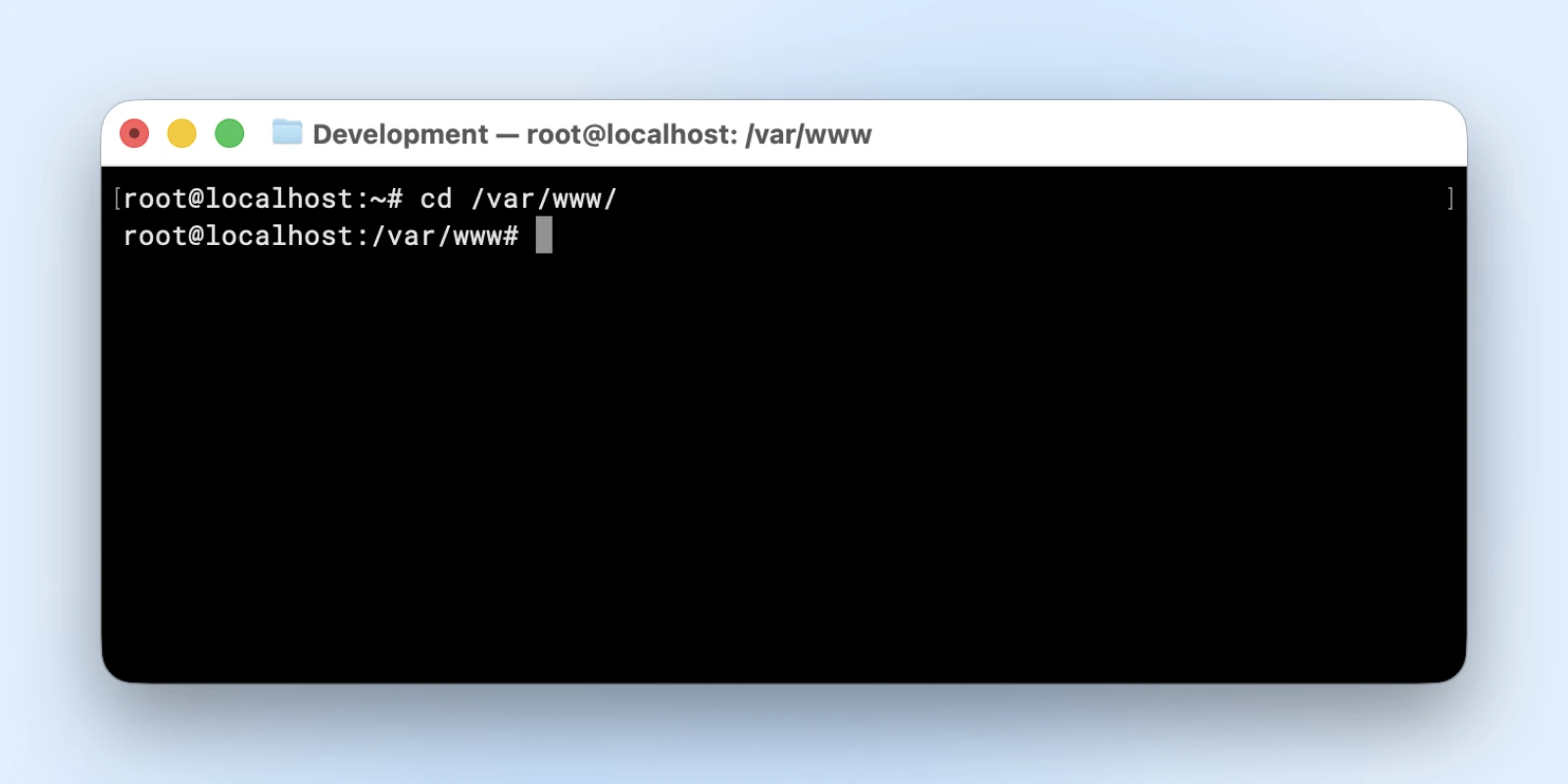
This strikes you on to your web site’s important listing, the place most information are saved.
File and Listing Administration
4. mkdir: Creates new directories
It stands for “Make Listing,” and the fundamental syntax is “mkdir directory-name” to create a single folder.
You should utilize “mkdir -p” to create nested listing buildings in a single command, and it gained’t error if directories exist already.
mkdir -p /var/www/newsite/{public,logs,backups,ssl}
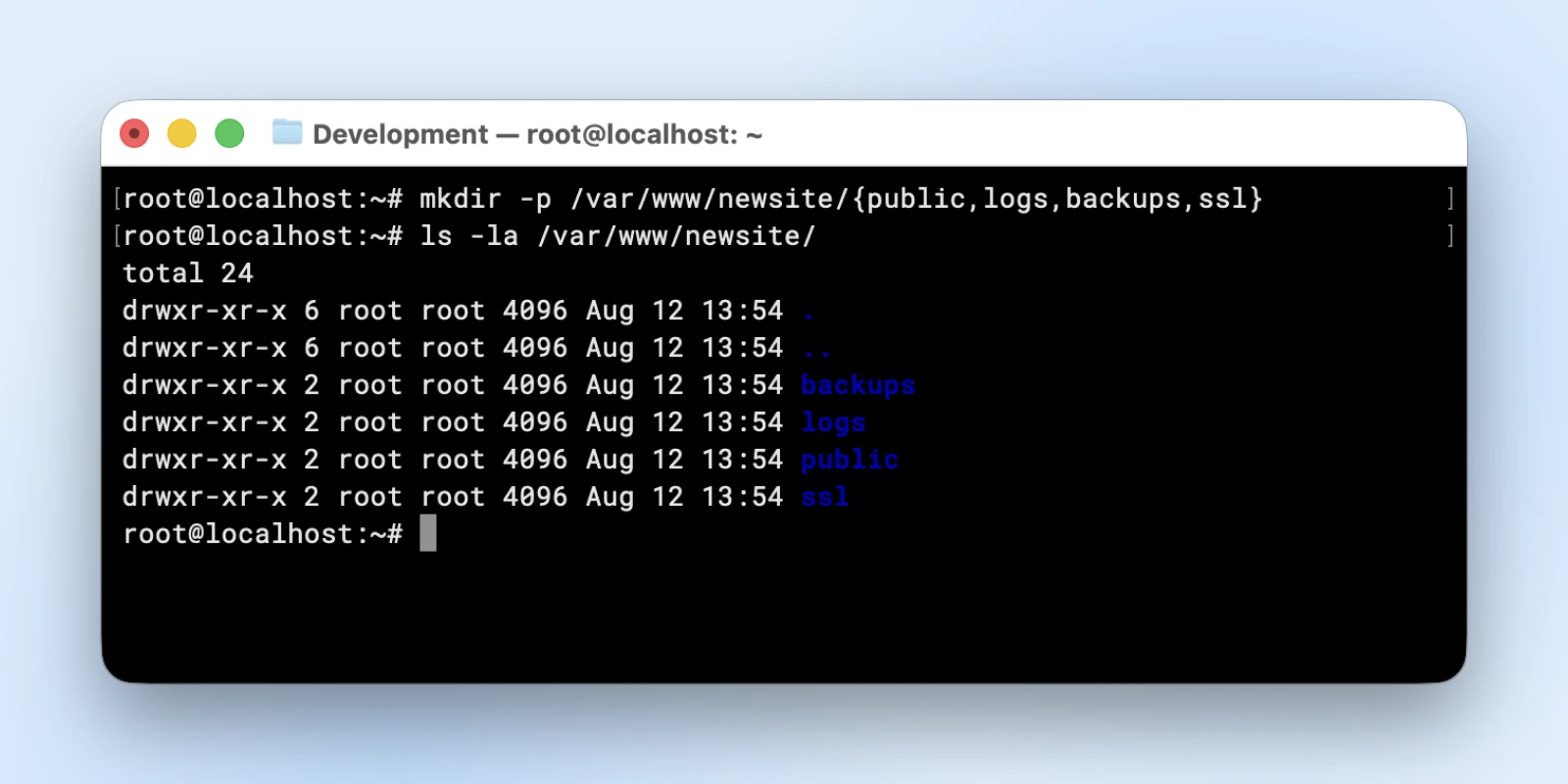
This creates an entire listing construction for a brand new web site with separate folders for public information, logs, backups, and SSL.
5. cp: Copies information and directories from one location to a different
The essential syntax is:
cp
Nonetheless, by default, the cp command doesn’t copy information inside folders and even nested folders.
You’ll want to make use of “cp -r” to repeat total listing timber recursively, which handles all subdirectories and their contents.
cp -r /var/www/manufacturing /var/www/staging
This creates an entire copy of your manufacturing web site for testing modifications earlier than deploying them reside.
6. mv: Strikes information and directories, or renames them
In contrast to copying, this removes the unique file, and you’ll transfer to completely different directories or rename information in the identical location.
Right here’s the fundamental syntax:
mv
To maneuver the file elsewhere, you should specify the total vacation spot path as under:
mv wordpress-6.3.2.zip /var/www/downloads/
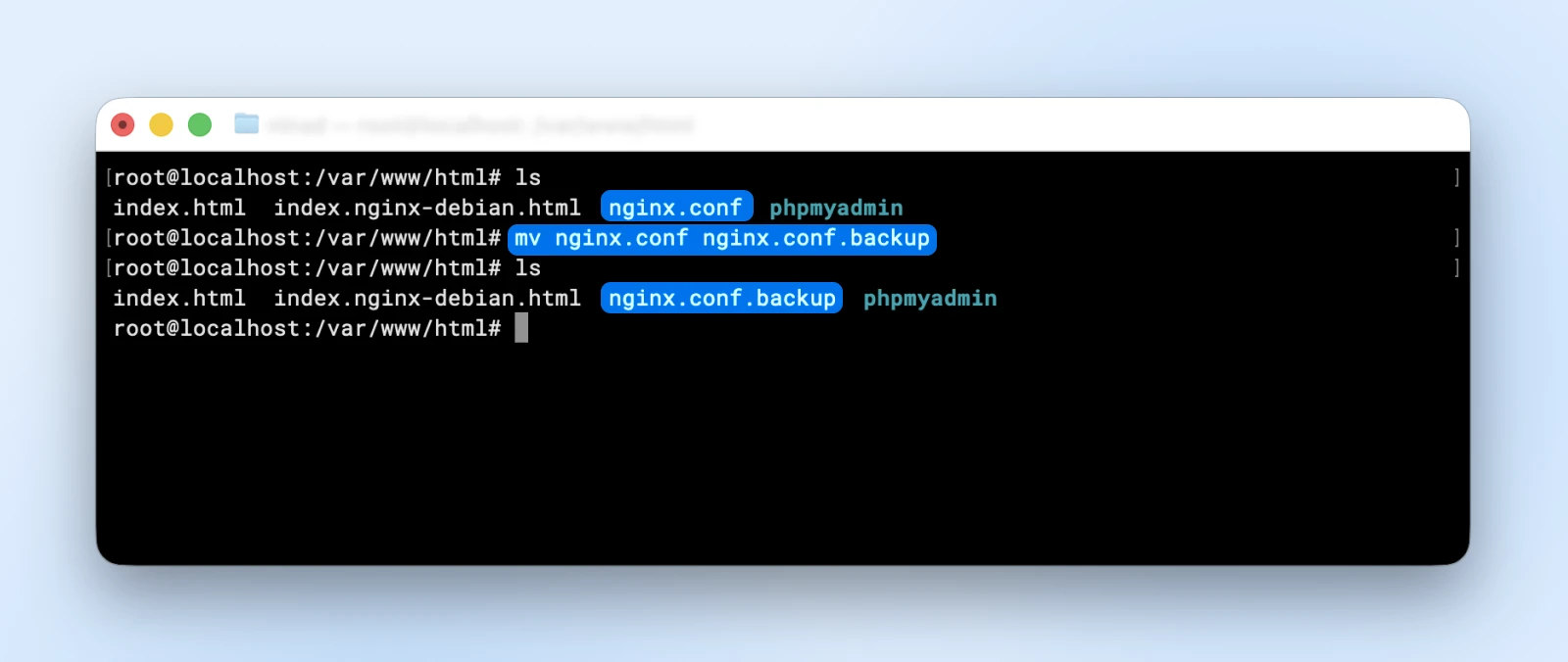
If you wish to rename a file, you’ll be able to simply “transfer” the file from one identify to a different identify in the identical listing:
mv nginx.conf nginx.conf.backup
File Content material Operations
7. cat: Shows the complete contents of a file in your terminal (Brief for concatenate)
The essential syntax is cat filename. This command is ideal for studying brief configuration information or checking the contents of scripts with out opening a textual content editor.
cat /var/www/html/wp-config.php
This shows your WordPress configuration file so you’ll be able to confirm database credentials or verify for syntax errors.
8. head: Reveals the primary few traces of a file
The default is 10 traces, however you’ll be able to specify a special quantity with “head -n 20.” That is helpful for checking massive log information with out displaying hundreds of traces in your terminal.
head -n 50 /var/log/nginx/entry.log
This reveals the primary 50 entries out of your internet server’s entry log to verify current visitors patterns.
9. tail: Reveals the previous couple of traces of a file
The tail command with none parameters reveals 10 traces, however “tail -f” repeatedly shows new traces as they’re added to the file. This makes it invaluable for monitoring log information in real-time whereas troubleshooting.
tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
This follows your error log in real-time, exhibiting new error messages instantly as they happen throughout web site operations.
Skilled Degree: Instructions for Managing Growth Workflows
As soon as you recognize your approach round, these professional-level instructions provide you with management over the dynamic components of your server. You possibly can monitor what’s operating, handle processes, and deal with system assets like a professional.

Course of Management and Monitoring
10. ps: Reveals presently operating processes in your system
Working “ps aux” shows all processes with detailed info, together with CPU and reminiscence utilization.
- a reveals processes for all customers.
- u supplies a user-friendly format.
- x contains processes not hooked up to terminals.
| the “pipe” passes the output from “ps aux” to the “grep” command, and I’ll cowl it within the file looking out part later.
ps aux | grep nginx
This full command outputs all NGINX-related processes, serving to you confirm your internet server is operating and establish any resource-heavy processes.
11. prime: Shows real-time system efficiency and operating processes
In contrast to “ps,” this command updates repeatedly, exhibiting reside CPU, reminiscence, and course of info. Press q to give up, okay to kill processes, and M to kind by reminiscence utilization.
prime
When your web site hundreds slowly, this reveals which processes are consuming assets. The load common and reminiscence utilization statistics assist establish system bottlenecks.
12. htop: Enhanced model of prime with higher visible interface
This supplies the identical performance as prime however with coloration coding, mouse help, and simpler navigation. Chances are you’ll want to put in it first with a sudo command, which we cowl down under.
htop
The colour-coded show makes it simpler to identify drawback processes at a look, and you’ll scroll by way of the method record extra simply.
13. kill: Terminates processes by their course of ID
Use kill
kill 1234
When a PHP course of will get caught consuming an excessive amount of CPU, discover its PID with ps aux or prime, then use kill to terminate it.
14. killall: Terminates all processes with a selected identify
You gained’t all the time know the PID since service names can differ from app names. The killall
killall php-fpm
This stops all PHP-FPM employee processes — helpful when you should restart your PHP handler utterly.
System Useful resource Monitoring
15. df: Reveals disk house utilization for all mounted filesystems
Working “df -h” shows disk utilization in human-readable format (GB, MB as an alternative of kibibytes). The above command might help you retain monitor of disk utilization so you’ll be able to keep away from disk full errors.
df -h
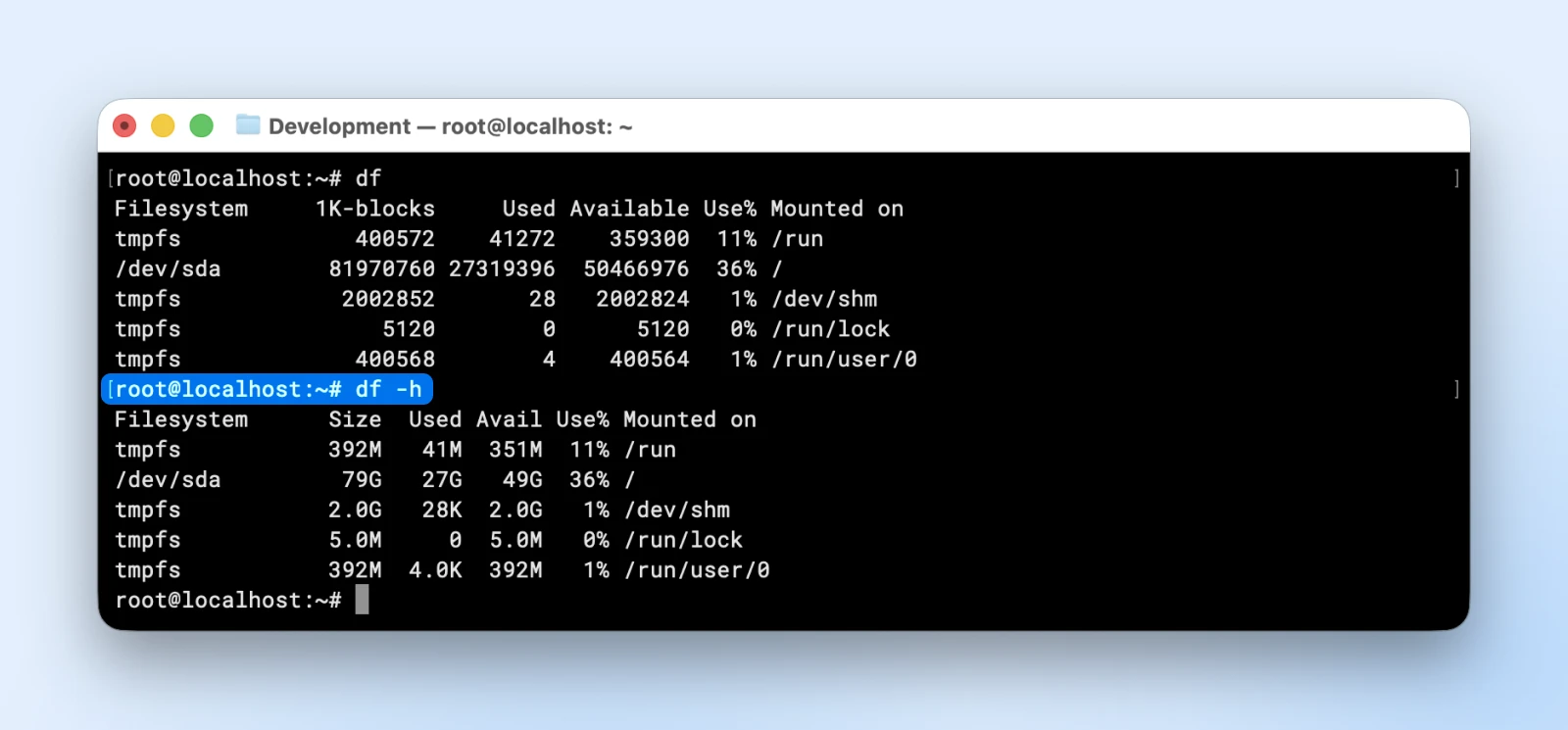
When you see the “use%” column with greater than 70% for any disk, it’s time to wash up the disk house or improve to bigger storage.
16. free: Shows reminiscence utilization together with RAM and swap house
With out parameters, the free command will present you knowledge in kibibytes (1 kibibyte is 1024 bytes).
Use “free -h” to see reminiscence statistics in human-readable format. This helps establish memory-related efficiency points earlier than they crash your functions.
free -h
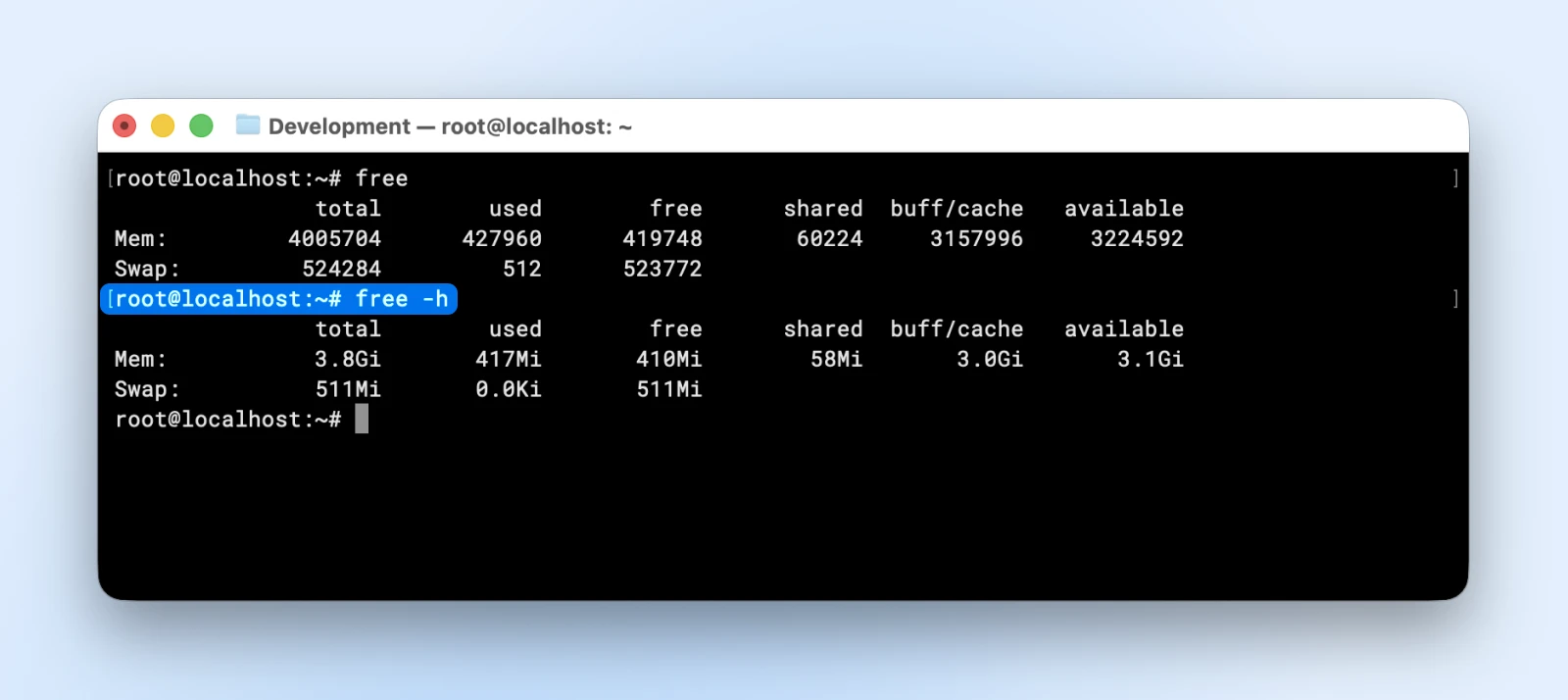
If “obtainable” reminiscence drops close to zero, your server will turn into unresponsive. This indicator tells you when so as to add extra RAM or optimize your functions.
17. du: Reveals disk utilization for particular directories
Working du -sh
du -sh /var/www/*
When you’re operating a number of web sites in your VPS, the above command will present you which of them web site consumes essentially the most house and helps you establish directories that might use cleanup
3. File Looking out and Textual content Processing
18. grep: Searches for textual content patterns inside information
Grep stands for “international common expression print.” I used the “grep” command with our “ps aux” command earlier than. Let me clarify what it really does.
This command can be utilized to search for textual content or regex patterns in massive textual content. Use grep “search time period”
grep -r "database_name" /var/www/html/
This finds all information containing your database identify, important for monitoring configuration references or troubleshooting connection points.
19. discover: Searches for information and directories primarily based on varied standards
This command helps you discover information in your path that match a selected identify or sample.
You should utilize discover
discover /var/www -name "*.log" -size +100M
This finds log information bigger than 100MB, serving to establish information that want rotation or cleanup to free disk house.
20. chmod: Adjustments file and listing permissions
File permissions on Linux could be complicated, and I can not clarify them intimately right here, however Crimson Hat wrote a complete article explaining file permissions.
When you perceive file permissions, you should utilize the “chmod” command to replace them.
Use chmod
“Permissions,” on this case, use numeric notation the place” 7=learn+write+execute,” “6=learn+write,” “4=learn solely.”
chmod 644 /var/www/html/wp-config.php
Giving 777 permissions to crucial information opens your server to safety vulnerabilities.
So that you want to pay attention to what permissions are completely mandatory and solely present these. Internet information usually want 644 permissions, whereas web site directories want 755 to run accurately.
Infrastructure Degree: Instructions for Manufacturing Environments
While you’re required to deal with the networking facet of your servers, these instructions can shortly separate competent directors from those that battle when actual points hit manufacturing web sites.
Community Diagnostics and Administration
21. ping: Assessments community connectivity and measures response time
The “ping” command checks in case your server can join to a different web site or server. You possibly can ping both a website identify or an IP deal with.
Utilizing simply ping
ping -c 4 yourdomain.com
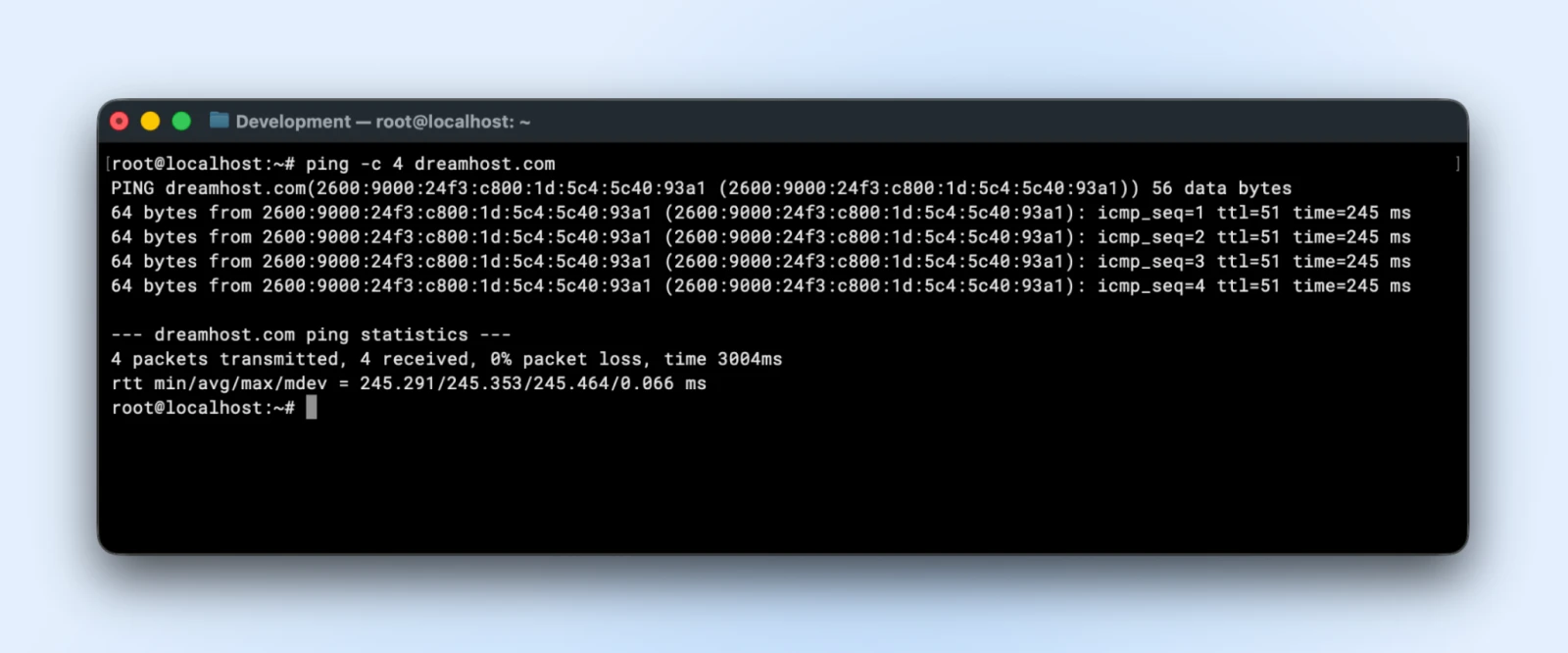
If ping fails solely, both DNS is damaged or there’s a community connectivity situation and you can begin narrowing down the problem from right here.
22. curl: Transfers knowledge to or from servers utilizing varied protocols
While you’re within the terminal, fetching an internet site and downloading packages is kind of tough. You don’t have a browser or a UI linked.
This command has quite a lot of parameters, so chances are you’ll need to undergo this official curl utilization tutorial to know it utterly.
However for checking if an internet site is responding, you solely want the “-I” (that’s uppercase i) parameter. This parameter helps curl fetch HTTP headers as an alternative of fetching the total HTML from the web site.
curl -I https://yourdomain.com
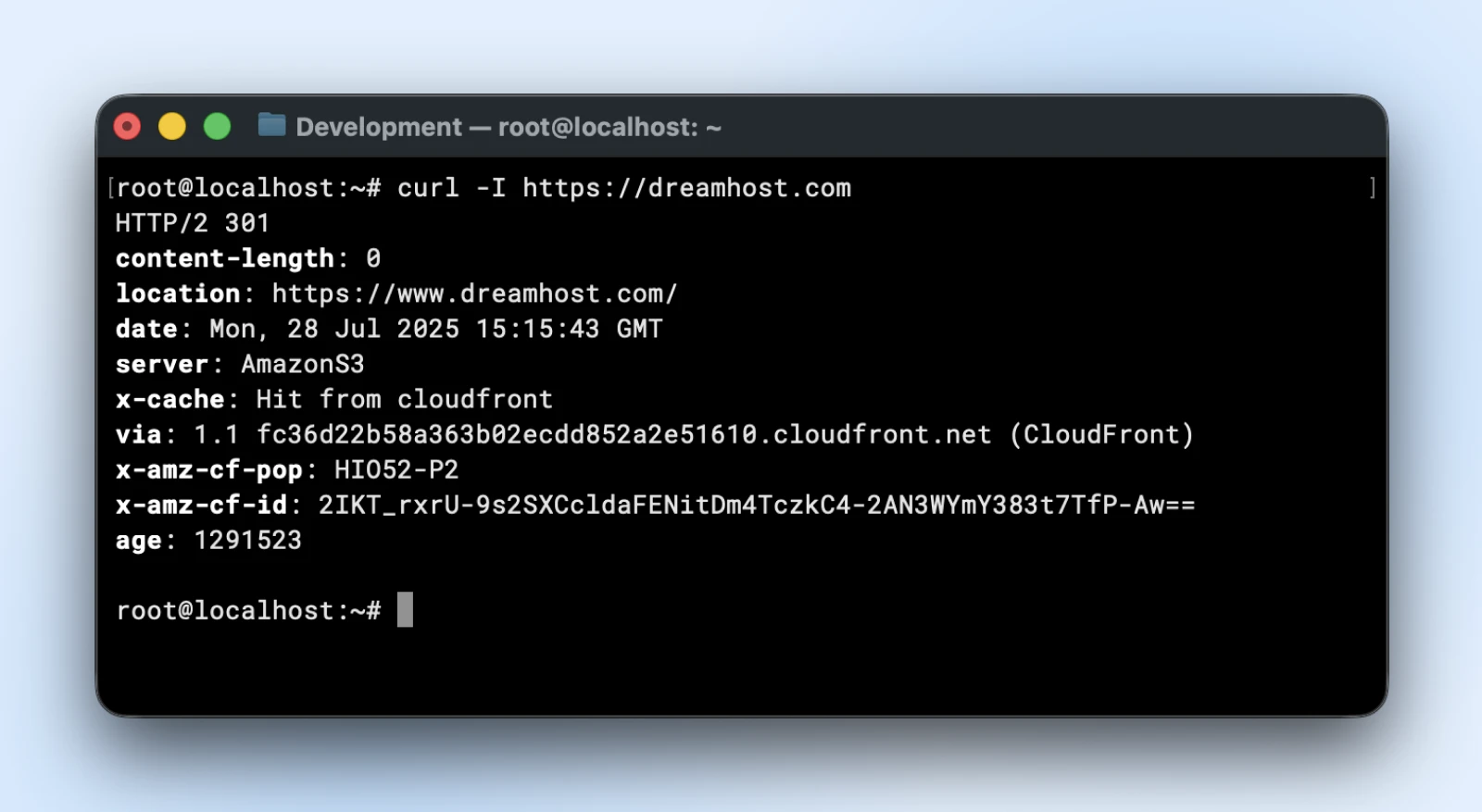
This reveals HTTP standing codes (“200=success,” “404=not discovered,” “500=server error”) and response headers, revealing points browsers would possibly conceal.
23. netstat: Reveals community connections and listening companies
Netstat is one more in depth command that helps you monitor your community connections, verify which ports are open in your server, which companies are listening on which particular ports, and much more.
Right here’s a easy information from IBM that reveals you some frequent netstat utilization.
For server use, you’d principally want the “netstat -tlnp command” to show listening community connections.
The flags imply:
- “-t” TCP connections
- “-l” listening solely
- “-n” numerical addresses
- “-p” course of IDs
netstat -tlnp | grep :80
This confirms your internet server is listening on port 80. If nothing seems, your internet server isn’t operating or configured correctly.
24. ss: A contemporary alternative for netstat with higher efficiency
Whereas netstat has been the legacy instrument that continues to work, it may be slower for those who’re on an especially busy server. The “ss” command got here in to repair that.
You should utilize related parameters as netstat with the ss command and obtain the output a lot quicker.
ss -tlnp | grep :443
This checks in case your internet server is listening for SSL connections on port 443, important for HTTPS web sites.
Safety and Entry Management
25. sudo: Executes instructions with elevated privileges
Sudo, brief for “tremendous consumer do,” allows you to carry out administrative duties with out switching to the basis consumer utterly. It helps run instructions with accountability and decreased threat.
When you change to the “root” account, you may have full management over your server and may by chance delete information, together with having the ability to delete the working system, whereas it’s operating.
So, sudo saves us from “suc” accidents. Simply prepend the command to any admin command and it’ll ask you to your password.
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Administrative duties like restarting companies require elevated privileges. Utilizing sudo is safer than logging in as root straight.
Do observe that your consumer must have the sudo permissions earlier than utilizing the sudo command.
26. chown: Adjustments file and listing possession
In Linux, each file is owned by a consumer and a bunch. You possibly can all the time change who owns the file through the use of the chown command. You should utilize chown
As an example, internet servers have to personal web site information to serve them correctly.
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/
This command is useful if you’re importing information through FTP. These information can are available in with the unsuitable possession, and you should utilize chown to vary that.
27. ssh-keygen: Generates SSH key pairs for safe authentication
SSH keys are way more safe than passwords for server entry. The SSH key sits in your laptop with out ever being despatched to the server, so a hacker watching your community won’t ever see the important thing that helped you log in.
Working “ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096” creates private and non-private key information.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your@e-mail.com"
This creates a “4096-bit RSA” key pair. Copy the general public key to servers for passwordless authentication and automatic deployments.
28. ufw: Ubuntu’s uncomplicated Firewall for fundamental server safety
Each server wants an excellent firewall setup. Most Linux servers include the ufw firewall, or it may be simply put in.
Upon getting it, run the ufw allow command to activate the firewall, then ufw enable
ufw allow
ufw enable 22
ufw enable 80
ufw enable 443
This enables SSH (22), HTTP (80), and HTTPS (443) visitors whereas blocking every part else, offering fundamental however efficient server safety.
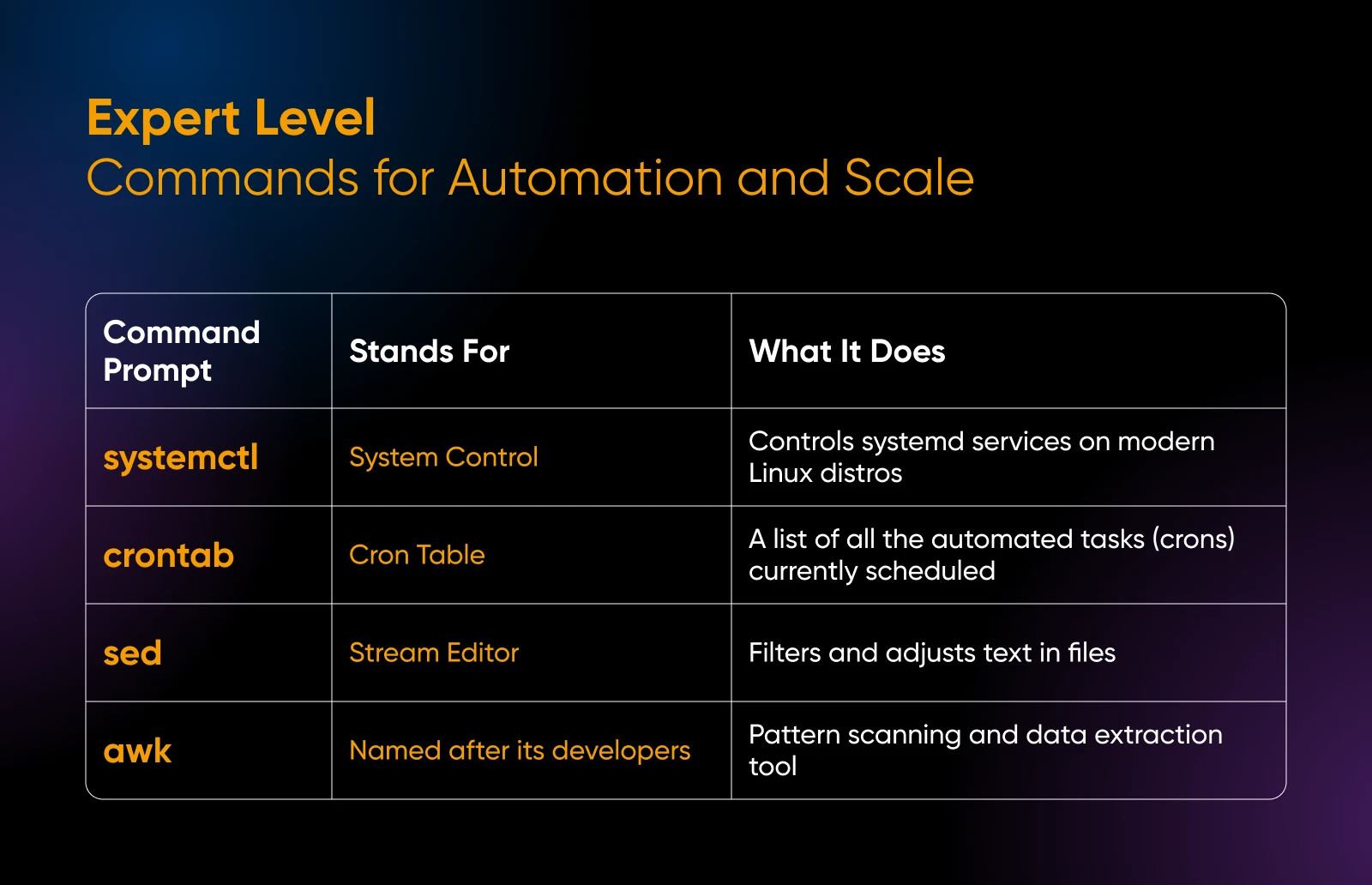
Professional Degree: Instructions for Automation and Scale
These instructions enable you to with automation and superior system administration for managing web sites at scale.
Service Administration
29. systemctl: Controls systemd companies on fashionable Linux distributions
Use systemctl
systemctl standing nginx
systemctl restart mysql
The primary command reveals detailed NGINX standing together with current log entries. The second restarts your database server to use any configuration modifications you might need made to the “mysql” configuration.
30. crontab: Schedules automated duties to run at particular occasions
You don’t need to get up in the midst of the night time to run server instructions. Cron jobs can do this for you.
To edit your private cron desk, run crontab -e and also you’ll see all of your current cron entries.
Duties are specified utilizing the format: minute, hour, day, month, weekday, and command.
0 2 * * * /usr/native/bin/backup-website.sh
As an example, the above cron job runs a backup script (“backup-website.sh”) day by day at 2 a.m.
You should utilize cron jobs for automated backups, log rotation, and upkeep duties and a lot extra in your manufacturing environments.
Superior Textual content Processing
31. sed: Stream editor for filtering and reworking textual content
Use sed ‘s/previous/new/g’
sed -i 's/old_database/new_database/g' /var/www/html/wp-config.php
This replaces all occurrences of “old_database” with “new_database” in your WordPress config file; helpful for database migrations.
32. awk: Sample scanning and knowledge extraction instrument
Working awk ‘{print $1}’
awk '{print $1}' /var/log/nginx/entry.log | kind | uniq -c | kind -nr | head -10
This extracts IP addresses from entry logs, counts them, and reveals the highest 10 guests to your web site.
Actual-World Utility Situations
Let’s have a fast overview, after which put these instructions collectively for frequent conditions you’ll face managing your VPS.
| Command Immediate: | Stands For: | What It Does: |
| ls | Checklist | Lists the contents of your present listing |
| pwd | Print working listing | Shows the total path of the place you might be situated |
| cd | Change Listing | Adjustments your present listing to the indicated location |
| mkdir | Make Listing | Creates a listing (a folder) within the requested location |
| cp | Copy | Copies information and directories from level A to level B |
| mv | Transfer | Strikes (or renames) information and directories |
| cat | Concatenate | Shows all of the contents of a file in your terminal |
| head | – | Reveals the primary 10 traces of a file |
| tail | – | Reveals the final 10 traces of a file |
| ps | Course of Standing | Reveals the processes operating in your system on the time it was run |
| prime | – | Shows a dynamic, real-time view of the processes operating in your system |
| htop | – | A extra UI centered model of “prime” |
| kill | – | Terminates the required course of |
| df | Disk Free | Shows the disk house utilization for all mounted file programs |
| free | Shows the quantity of free and used reminiscence within the system | |
| du | Disk Utilization | Shows the disk utilization for a selected listing |
| grep | World Common Expression Print | Searches for textual content patterns inside information |
| discover | – | Finds information and directories primarily based in your standards |
| chmod | Change Mode | Modifies file system permissions |
| ping | Packet Web Groper (however most individuals simply say “Ping”) | Checks in case your server can join to a different web site or server |
| curl | Consumer URL | Transfers knowledge to or from servers |
| netstat | Community Statistics | Shows community connections and listening companies. |
| ss | Socket Statistics | An up to date model of netstat |
| sudo | Tremendous Consumer Do | Executes instructions with elevated privileges |
| chown | Change Proprietor | Adjustments file and listing possession |
| ssh-keygen | Safe Shell Key Technology | Generates SSH Key pairs for safer authentication |
| ufw | Uncomplicated Firewall | A user-friendly firewall for fundamental server safety |
| systemctl | System Management | Controls systemd companies on fashionable Linux distros |
| crontab | Cron Desk | An inventory of all of the automated duties (crons) presently scheduled |
| sed | Stream Editor | Filters and adjusts textual content in information |
| awk | Named after its builders | Sample scanning and knowledge extraction instrument |
When Your Web site Hundreds Slowly
Begin by checking what’s consuming your server assets.
Run prime or htop to see which processes are utilizing essentially the most CPU and reminiscence. You’re in search of any processes consuming over 50% of your assets and if any of them could be killed.
If useful resource utilization appears regular, verify your obtainable disk house with “df -h.” When you discover utilization exceeding 90% on any filesystem, release house as quickly as attainable. Every little thing drastically slows down when your server is full.
Subsequent, confirm your internet server is definitely operating correctly.
Use ps aux | grep nginx (or ps aux | grep apache for those who’re utilizing Apache) to verify your internet server processes are lively and responding.
Verify your error logs whereas testing your website.
Run tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log in a single terminal, then go to your web site in a browser window. If there are any errors operating your website, you must see them instantly seem in your terminal.
Lastly, take a look at your web site’s response time straight from the server with curl -I https://yoursite.com. This bypasses any community points and tells you precisely how lengthy your server takes to reply.
Setting Up a Safe Growth Surroundings
Create a devoted consumer account for growth work as an alternative of utilizing root for every part:
sudo adduser devuser
Arrange a correct listing construction to your staging website. This retains growth information organized and separate from manufacturing:
mkdir -p /var/www/staging/{public,logs,backups}
Repair the possession so your internet server can entry the information correctly:
chown -R devuser:www-data /var/www/staging
Set applicable permissions – 755 permits the proprietor to learn/write/execute whereas giving others learn and execute entry:
chmod -R 755 /var/www/staging
Configure your firewall to permit solely important companies. Begin by permitting SSH so that you don’t lock your self out:
sudo ufw enable 22
Permit internet visitors on the usual HTTP and HTTPS ports:
sudo ufw enable 80
sudo ufw enable 443
Allow the firewall to begin blocking unauthorized connections:
sudo ufw allow
Command Mixtures That Present Actual Proficiency
Superior customers mix instructions to unravel complicated issues:
The under command finds nginx processes, extracts their PIDs, and kills them multi function line:
ps aux | grep nginx | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9
This discover command robotically removes log information older than 7 days to free disk house:
discover /var/log -name "*.log" -mtime +7 -delete
This mixed du command reveals the 5 largest directories in your internet root, sorted by measurement:
du -sh /var/www/* | kind -hr | head -5
When you’re getting 404 errors, run this command to rely them in your entry log to establish damaged hyperlinks:
grep -c "404" /var/log/nginx/entry.log
So, What Comes Subsequent
When you’re comfy with these 30 instructions, you’ll need a high quality VPS supplier that’s quick and versatile whereas offering full management to your rising abilities.
DreamHost’s VPS internet hosting provides simply that. You get full root entry to experiment safely, SSD storage that makes file operations lightning-fast, and scalable assets when your tasks outgrow their present limits.
We additionally embrace automated backups so you’ll be able to experiment fearlessly, and our help workforce understands Linux environments whenever you need assistance with complicated configurations.

Take Cost with Versatile VPS Internet hosting
Right here’s how DreamHost’s VPS providing stands aside: 24/7 buyer help, an intuitive panel, scalable RAM, limitless bandwidth, limitless internet hosting domains, and SSD storage.
Did you get pleasure from this text?

